Introduction
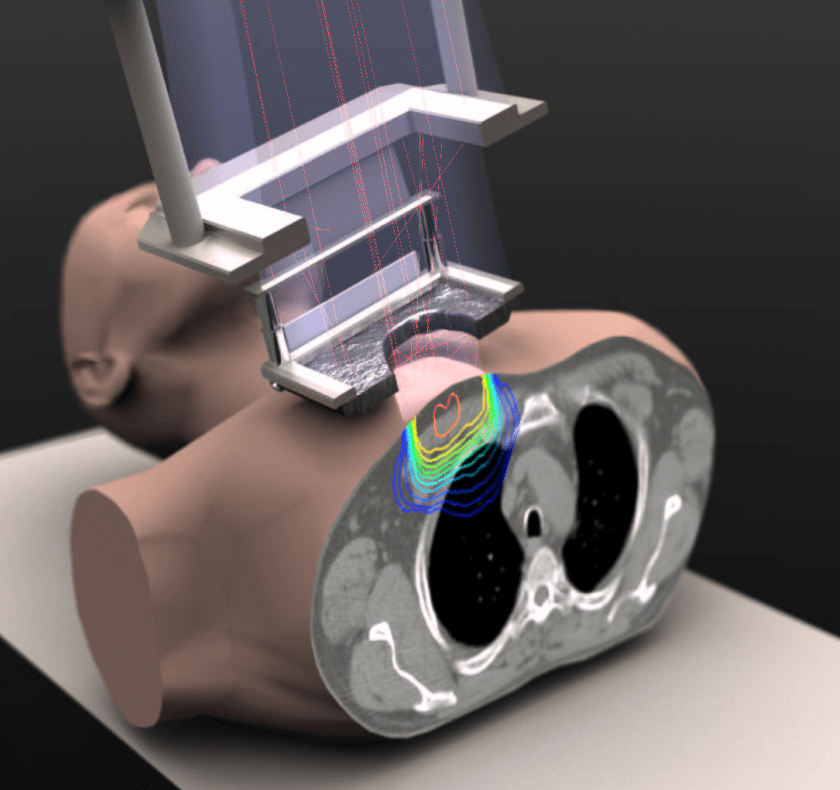
In the field of radiotherapy, technological advancements play a pivotal role in improving cancer treatment outcomes. One such game-changing innovation is “Parallel Computing.” By harnessing the immense power of multiple processors working together, parallel computing has opened new frontiers in radiotherapy, enabling faster and more precise treatment planning and delivery. Let’s delve into the world of parallel computing and explore its transformative impact on radiotherapy.
Understanding Parallel Computing in Radiotherapy
Parallel computing is like having a team of super-fast computers working together as one. Instead of relying on a single processor to perform complex calculations, parallel computing splits the workload among multiple processors, allowing tasks to be completed simultaneously. In the context of radiotherapy, this means that intricate treatment planning and delivery processes can be accelerated, reducing the time patients spend in the treatment room and enhancing overall treatment efficiency.
How Parallel Computing Advances Radiotherapy
- Accelerated Treatment Planning: Radiotherapy treatment planning involves complex computations to determine the optimal radiation dose distribution that targets cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues. Parallel computing expedites these calculations, generating treatment plans in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. Oncologists can quickly evaluate various treatment options and fine-tune plans to tailor therapy for individual patients, ensuring optimal outcomes.
- Real-Time Image Processing: During treatment, it’s vital to verify the tumor’s position and adjust radiation delivery accordingly. Parallel computing allows real-time image processing, enabling radiation therapists to monitor the tumor’s movement and dynamically adjust the treatment beam, ensuring precise targeting even if the tumor shifts slightly during the session.
- Monte Carlo Simulations: Parallel computing significantly accelerates complex Monte Carlo simulations, a vital tool in radiotherapy to model radiation interactions with biological tissues. By simulating millions of particle interactions in parallel, researchers gain deeper insights into dose distributions and radiation safety, enhancing treatment accuracy and patient care.
- Big Data Analytics: Radiotherapy generates vast amounts of data from patient imaging, treatment plans, and outcomes. Parallel computing empowers researchers to process and analyze this data swiftly, leading to the discovery of patterns and trends that can inform the development of personalized treatment approaches.
Benefits of Parallel Computing in Radiotherapy
- Enhanced Treatment Precision: Parallel computing enables high-resolution dose calculations and improved target conformality, reducing the risk of damaging healthy tissues and minimizing side effects.
- Reduced Treatment Time: Faster treatment planning and delivery processes lead to shorter overall treatment times, easing patient burden and increasing treatment capacity.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: The precision and efficiency of parallel computing contribute to better treatment outcomes and increased chances of cancer control.
Conclusion
Parallel computing has emerged as a revolutionary force in radiotherapy, unleashing the potential to significantly advance cancer treatment. By accelerating treatment planning, enabling real-time image processing, and enhancing data analysis, parallel computing optimizes radiation therapy with unprecedented precision and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, parallel computing will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of radiotherapy, improving patient care, and bolstering the fight against cancer.
Author: Abdelhai Ben Ali, PhD
Supporting documents
- Luke R. Mason et al. A parallel optimisation approach for the realisation problem in intensity modulated radiotherapy treatment planning. Computational Optimization and Applications, 60, pages441–477 (2015). doi.org/10.1007/s10589-014-9670-z, read the article.
- Hui Lin et al., Modeling of Radiotherapy Linac Source Terms Using ARCHER Monte Carlo Code: Performance Comparison for GPU and MIC Parallel Computing Devices. EPJ Web of Conferences 153, 04010 (2017). doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/201715304010, read the article.

2 responses to “Advancing Radiotherapy with Parallel Computing”
I want make a PhD research on this topic
LikeLiked by 1 person
This is really a great topic for a PhD! You can prepare some ideas as a short proposal of what you want to do and communicate with university Faculty members and heads of laboratories. Hopefully, you will get a response(s) from potentially interested Faculty to have you join their lab.
LikeLike